
In the modern world, we rely on various devices and technologies to communicate with each other over long distances. These devices and technologies use computer networks, which are systems of interconnected computers that exchange data and information. However, data and information cannot be transmitted from one device to another without following some rules and methods. These rules and methods are collectively known as transmission modes.
Transmission modes are the ways of transferring data over a communication channel, which is the medium that connects the devices on a network. A communication channel can be a physical wire, a cable, or a wireless medium, such as radio waves, microwaves, or infrared signals. Transmission modes determine how data is transmitted over a communication channel, such as the direction, speed, capacity, and quality of data flow.
There are different types of transmission modes, each with its own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Some of the most common transmission modes are given below:
- Simplex,
- Half-Duplex
- Full-Duplex
These modes differ in the direction and capacity of data flow between the devices.
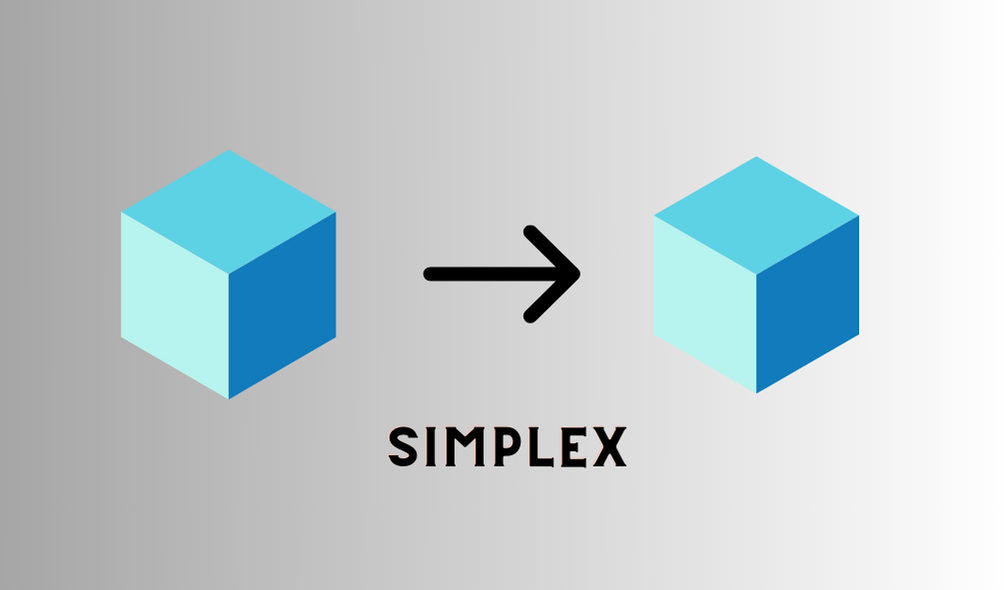
Simplex Transmission Mode
Simplex mode is a type of transmission mode in computer networks, where data can flow in only one direction. A device in simplex mode can either send or receive data, but not both. The entire capacity of the communication channel is used for one direction of data flow. Simplex mode is simple, reliable, and cost-effective, but it does not allow feedback or bidirectional communication.
Applications Of Simplex Transmission Mode
- Keyboard: A keyboard can only send input to a computer, but cannot receive any output from it.
- Radio station: A radio station can only broadcast signals to the listeners, but cannot receive any feedback from them.
- Smart speakers: A smart speaker can only play audio from a source, but cannot record any sound from the environment.
Pros and Cons Of Simplex Transmission Modes
| Pros | Cons |
| Simplex mode does not require any complex hardware or software to implement. It also avoids any interference that may occur in bidirectional modes. It is suitable for low-budget applications that do not need feedback or interaction. | Simplex mode does not allow any data flow in the opposite direction. This limits the functionality and flexibility of simplex mode for applications that need bidirectional communication. |
| Simplex mode does not require any synchronization between the sender and the receiver. It does not use any handshaking protocols to establish or terminate the communication. It also does not use any flow control or congestion control techniques to regulate the data flow. | Simplex mode is not very widely used in modern computer networks. It is mostly used for specialized applications that do not need bidirectional communication. It is also not interoperable with other modes of transmission that use bidirectional communication. |
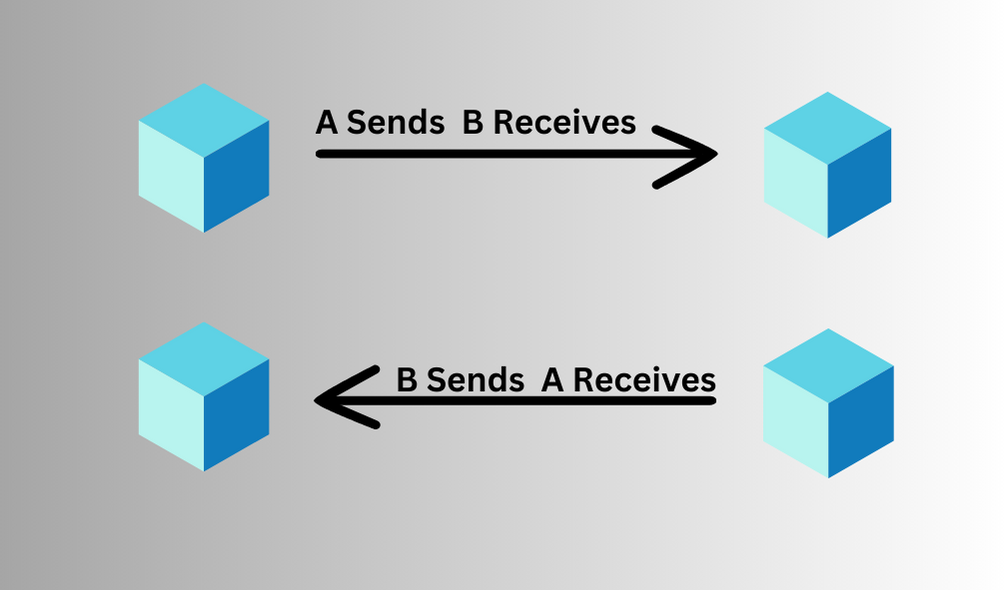
Half Duplex Transmission Mode
Half-duplex mode is a type of transmission mode in computer networks, where data can flow in both directions, but not at the same time. When one device is sending, the other can only receive, and vice versa. The half-duplex mode is used in cases where there is no need for communication in both directions at the same time. The entire capacity of the channel can be utilized for each direction alternately
Applications of Half-Duplex Transmission Mode
- Walkie-talkie: A walkie-talkie is a handheld device that can send and receive voice messages over a short distance. Only one party can speak at a time, and the other party has to listen. Speaking simultaneously will create interference and distortion in the communication.
- Telephone: The telephone can operate in half-duplex or full-duplex mode, depending on the type of connection. In half-duplex mode, the user has to press a button or a switch to change between talking and listening modes.
- Wireless microphone: A wireless microphone is a device that can transmit audio signals wirelessly to a receiver or a speaker. It uses radio waves or infrared signals to send the signals. In half-duplex mode, the microphone can only transmit signals, and cannot receive any feedback or control signals from the receiver
Pros and Cons Of Half Duplex Transmission Mode
| Pros | Cons |
| Half-duplex mode enables data to flow in both directions between the devices, but not at the same time. This allows the devices to exchange information and feedback, and to perform interactive and cooperative tasks. | Half-duplex mode restricts the data flow to one direction at a time. This means that the devices have to switch between transmitting and receiving modes, and cannot do both simultaneously. |
| Half-duplex mode requires less hardware and software to implement than full-duplex mode. It also avoids the complexity and cost of using two channels to support simultaneous data flow in both directions. | Half-duplex mode requires some coordination between the sender and the receiver. It also uses some flow control or congestion control techniques to regulate the data flow. This complicates the operation and management of half-duplex mode. |
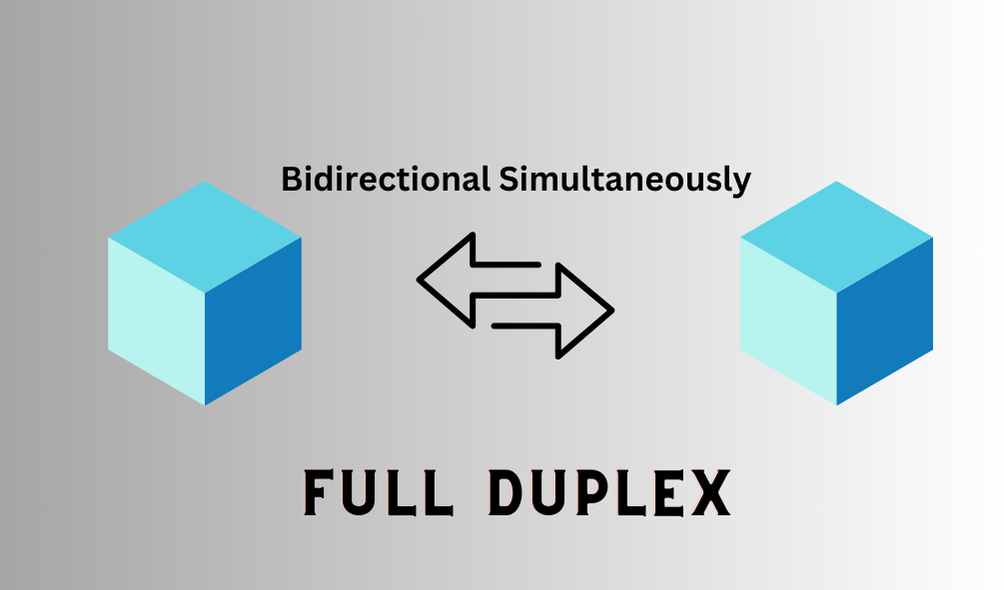
Full Duplex Transmission Mode
Full-duplex mode is a type of transmission mode in computer networks, where data can flow in both directions simultaneously. Both devices can send and receive data at the same time, without any interference or delay. The full-duplex mode requires two channels or multiplexing to share the capacity of the communication channel between the two directions. Full-duplex mode is reliable, fast, and suitable for applications that need continuous and interactive communication.
Applications of Full Duplex Transmission Mode
- Mobile phone: It uses frequency-division duplexing (FDD) or time-division duplexing (TDD) to separate the uplink and downlink signals on different time slots. The mobile phone can operate in full-duplex mode, allowing the user to talk and listen at the same time.
- Internet: It uses packet switching to divide and route the data into small units called packets. The internet can support full-duplex communication, allowing the devices to send and receive data simultaneously.
- Video conferencing: Video conferencing is a technology that allows two or more people to communicate visually and audibly over a network. It uses audio and video compression to reduce the bandwidth and latency of the data transmission.
Pros and Cons Of Full Duplex Transmission Mode
| Pros | Cons |
| Full-duplex mode provides a high level of reliability and accuracy, as there is no need for error correction mechanisms. The devices can verify and acknowledge the data transmission in real-time, and detect and resolve any errors or collisions. | Full-duplex mode is the most expensive mode, as it requires two communication channels to support simultaneous data flow in both directions. It also requires more hardware and software to implement and manage than half-duplex or simplex modes. |
| The devices can utilize the full bandwidth and speed of the channel for both directions. This improves the performance and quality of full-duplex mode for applications that need high data rate and low latency. | The devices can utilize the full bandwidth and speed of the channel in both directions. This improves the performance and quality of full-duplex mode for applications that need high data rate and low latency. |
FAQs
- What is the difference between frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) and time-division multiplexing (TDM) in full-duplex mode?
Answer: FDM and TDM are two multiplexing techniques that allow full-duplex communication on a single channel. FDM divides the channel into multiple frequency bands and assigns each band to a different direction of data flow. TDM divides the channel into multiple time slots and assigns each slot to a different direction of data flow.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of broadcast and multicast modes in computer networks?
Answer: Broadcast mode and multicast mode are two types of transmission modes that allow data to be sent from one device to multiple devices on a network. Broadcast mode sends data to all devices on the network, regardless of their interest or need. Multicast mode sends data to a group of devices on the network, based on their subscription or request. Broadcast mode is simple and efficient, but it can cause congestion and waste of bandwidth.
- What are the applications and challenges of anycast mode and unicast mode in computer networks?
Answer: Anycast mode and unicast mode are two types of transmission modes that allow data to be sent from one device to another device on a network. Anycast mode sends data to the nearest device on the network, based on some criteria such as distance, latency, or load. Unicast mode sends data to a specific device on the network, based on its unique address. Anycast mode is useful for load balancing, fault tolerance, and content delivery. Unicast mode is useful for point-to-point communication, privacy, and reliability. Anycast mode can cause ambiguity, inconsistency, and routing issues. The unicast mode can cause congestion, delay, and resource consumption.
Take a glance at another intriguing article where we’ve delved extensively into distinguishing between Full Duplex and Half Duplex.
